Today in this article we shall discuss with you about Mathematical Symbols in detail.
In the earlier post you have read about Shortcut Keys for Computer in detail.
Mathematical Symbols-
Useful List of Math Symbols in English
Learn useful Mathematical symbols (equal sign ‘=’, not equal sign ‘≠’, approximately equal sign ‘≈’…) with examples. In English, there are certain symbols, which are used in math and each of these has a name.
It is very useful to be able to recall the names of these symbols.
This will greatly assist you in your conversation and especially when looking at written English.
Perhaps you are a student, these math symbols will be extremely handy to have in your arsenal.
Not only that, but by being able to state the names of these symbols, you will begin to sound more like a native speaker.
List of Mathematics Symbols-
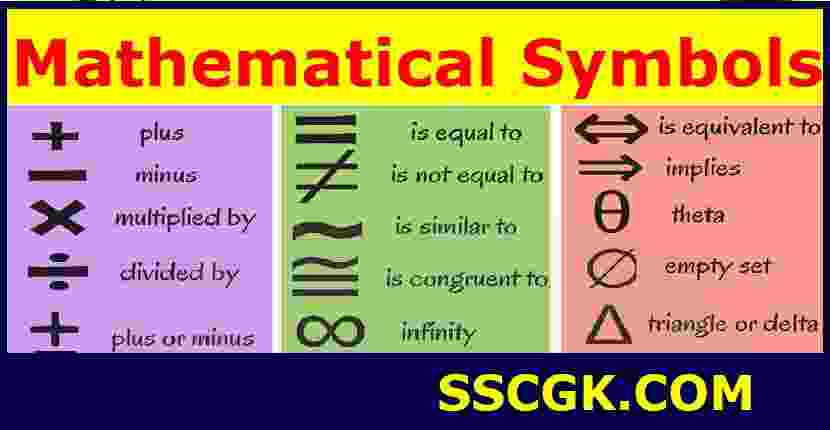
1.Addition
2.Subtraction
3.Multiplication
4.Division
5.Plus-minus
6.Strict inequality
7.Equality
8.Inequation
9.Tilde
10.Congruence
11.Infinity
12.Inequality
13.Material equivalence
14.Material implication
15.Theta
16.Empty set
17.Triangle or delta
Mathematical Symbols-
18.For all
19.Pi constant
20.Integral
21.Intersection
22.Union
23.Factorial
24.Therefore
25.Square root
26.Perpendicular
27.Exists
28.Line
29.Line segment
30.Ray
31.Right angle
32.Angle
33.Summation
34.Braces (grouping)
35.Brackets
36.Parentheses (grouping)
मैथ के चिह्न उदाहरण सहित –
Learn these Math symbols with examples to improve your Math vocabulary in English.
No.- 1. Addition
– Read as: Plus/ Add
Example: “Three plus three equals six.” (3 + 3 = 6)
No.- 2.Subtraction
– Read as: Minus
Example: “Three minus one equals two.” (3 – 1 = 2)
No.- 3.Multiplication
– Read as: Times/ Multiplied by
Example: “Four multiplied by five is twenty.” (4 x 5 = 20)
No.- 4.Division
– Read as: Divided by
Example: “Nine divided by three is three.” (9 : 3 = 3)
No.- 5.Plus-minus
– Read as: Plus or minus
Example: “Three plus or minus two equals five or one.” (3 ± 2 = 5 or 1)
No.- 6.Strict inequality
– Read as: Is greater than
Example: “Three is greater than two.” (3 > 2)
– Read as: Is less than
Example: “Two is less than three.” (2 < 3)
No.- 7.Equality
– Read as: Is equal to
Example: “Four is equal to three plus one.” (4 = 3 + 1)
No.- 8.Inequation
– Read as: Is not equal to
Example: “Four is not equal to three.” (4 ≠ 3)
No.- 9.Tilde
– Read as: Is similar to
No.- 10.Congruence
– Read as: Is congruent to
No.- 11.Infinity
– Read as: Infinity
No.- 12.Inequality
– Read as: Is greater than or equals
Example: “a is greater than or equal to b.” (a ≥ b)
– Read as: Is less than or equals
Example: “a is less than or equal to b.” (a ≤ b)
No.- 13.Material equivalence
– Read as: Is equivalent to
No.- 14.Material implication
– Read as: Implies
No.- 15.Theta
– Read as: Theta
No.- 16.Empty set
– Read as: Empty set
No.- 17.Triangle or delta
– Read as: Triangle/ Delta
No.- 18.For all
– Read as: For all
No.- 19.Pi constant
Read as: Pi
No.- 20.Integral
Read as: Integral
Mathematical Symbols-
No.- 21.Intersection
Read as: Intersection of two sets
No.- 22.Union
Read as: Union of two sets
No.- 23.Factorial
Read as: Factorial
No.- 24.Therefore
Read as: Therefore
No.- 25.Square root
– Read as: Square root of
No.- 26.Perpendicular
Read as: Is perpendicular to
No.- 27.Exists
Read as: Exists
28.Percent
Read as: Percent
No.- 29.Line
– Read as: Line AB
No.- 30.Line segment
– Read as: Segment AB
No.- 31.Ray
– Read as: Ray AB
No.- 32.Right angle
– Read as: Right angle
No.- 33.Angle
– Read as: Angle
No.- 34.Summation
– Read as: Sum of/ Sigma
No.- 35.Braces (grouping)
– Read as: Braces
No.- 36.Brackets
– Read as: Brackets
No.- 37.Parentheses (grouping)
– Read as: Parentheses